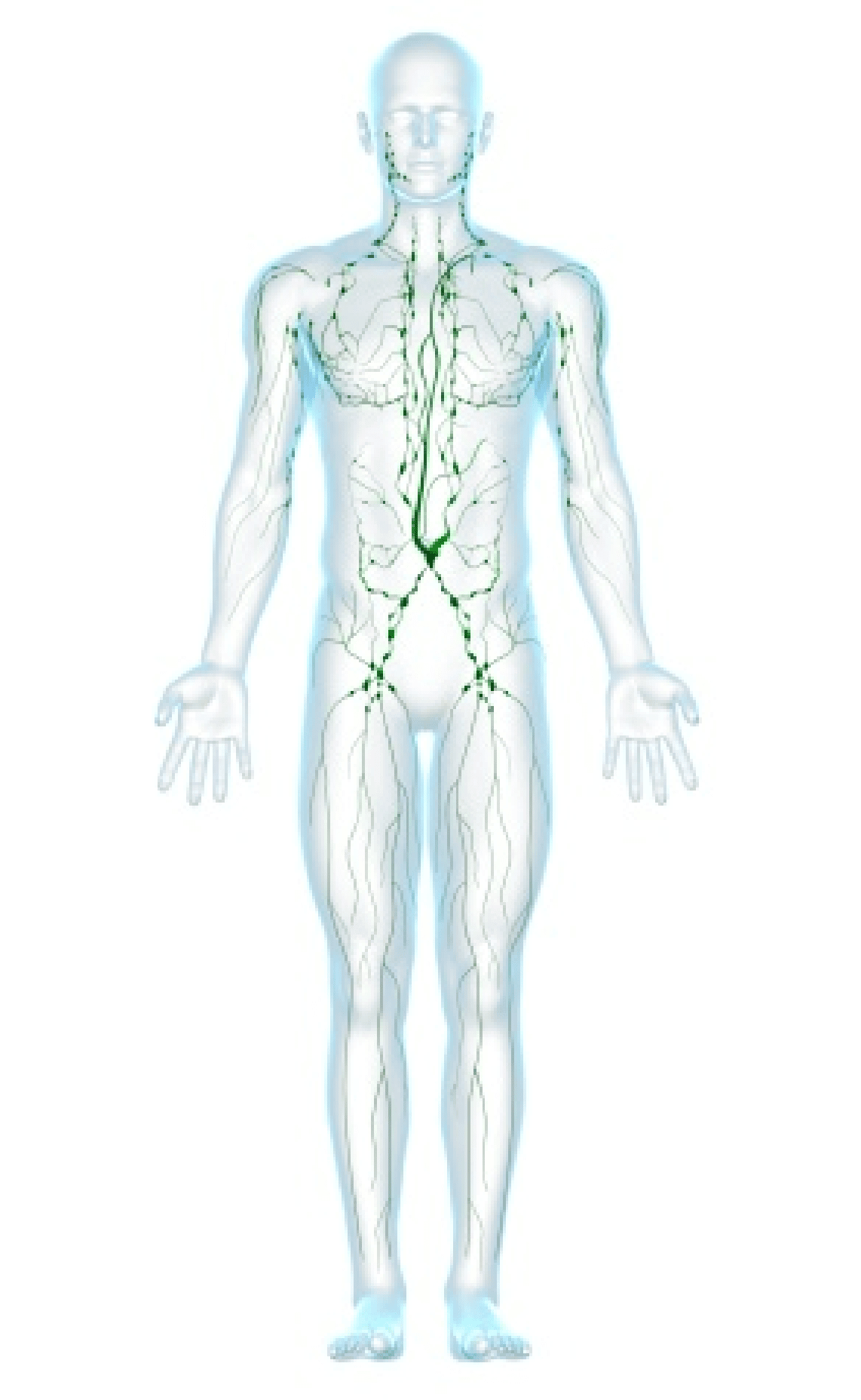
About lymphoma
Lymphoma is cancer found in a group of tissues, vessels, and organs called the
lymphatic system.
This system works with your bloodstream to clear anything that’s not supposed to
be there. It also works with your immune system, the system in the body that
protects your body from outside invaders. It helps you get better when you’re not
feeling well.
The type of lymphoma you are diagnosed with will fall into either the Hodgkin’s or
Non-Hodgkin’s category.
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is the 5th most common type of cancer found in adults in the US.
What is diffuse large B-cell lymphoma?
DLBCL is a type of fast-growing Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It affects a type of white blood cell (lymphocyte) called B-cells.
B-cells make antibodies, fight infections, and are an important part of the lymphatic system.
When DLBCL grows, it may begin in the lymph nodes. Or it may begin in the areas outside the lymph nodes or the “extranodal sites.”
DLBCL may be found in 1 spot, which is known as “localized.” Or the cancer could spread throughout the body, which is referred to
as “generalized.”
DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in the world.
What is relapsed/refractory (r/r) DLBCL?
Relapsed cancer:
The cancer came back after past therapies worked
OR
Refractory cancer:
Therapy/therapies never worked or no longer work
DLBCL Symptoms
These may not be inclusive of all the symptoms of DLBCL.
The first sign of DLBCL is usually rapid swelling in the:
- neck
- underarms
- groin
- abdomen
It can also be identified by abdominal pain caused by enlarged lymph nodes.
Other symptoms (known as B-symptoms) include:
- night sweats
- chills
- unexplained fevers
- weight loss
It can also be identified by abdominal pain caused by enlarged lymph nodes.
DLBCL Relapse Symptoms
Signs of DLBCL relapse can be hard to find with scans or physical exams. These B-symptoms, along with enlarged lymph nodes, can be signs of DLBCL relapse.
Use the doctor discussion guide to aid conversations with your doctor
DLBCL Treatment
Treatments will vary per phase of cancer (relapsed or refractory). Other considerations for the types of treatments chosen are:
- overall health
- age
- other treatments you may be on at the same time
- whether the cancer has been treated before and which treatments were used
Get info on antibody-drug conjugate technology
Antibody-Drug Conjugate — Also called ADC. A substance made up of a monoclonal antibody (also called mAb) that is chemically linked to a drug. The mAb binds to specific proteins found on certain types of cells, including cancer cells. The drug enters these cells and kills them. Some ADCs are used to treat cancer.